Take Control of Cloud Costs and Maximise Cloud Benefits: Aptum Cloud Impact Study
Advice on choosing the best cloud infrastructure for workloads and avoiding unforeseen costs.
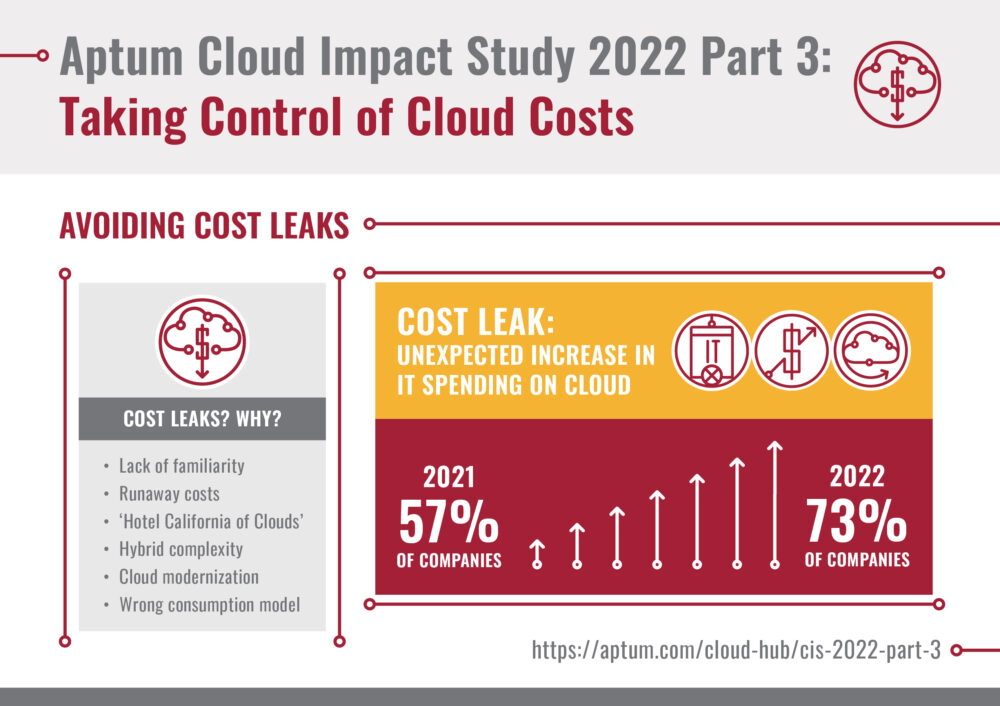
Aptum, a hybrid multi-cloud managed service provider, has announced Part 3 of its annual Cloud Impact Study 2022, titled Taking Control of Cloud Costs. The findings reveal cloud computing has resulted in higher-than-expected costs for 73% of IT decision-makers – a notable increase of 28% from just over half (57%) of companies in 2021. The report explores the common financial drivers behind cloud computing, and the causes of its unplanned expenses.
Overall, cloud computing has given respondents more control over IT expenditure, with more than half (63%) of respondents saying cloud transformation positively impacts IT spending, and the majority (86%) saying cloud technology is essential to their company’s financial security.
The operating expenditure (OpEx) payment structures of cloud computing allow organizations to pay for the compute and storage they use, while also monitoring monthly usage and spend. The study’s respondents concur: 71% believe cloud transformation positively impacts operational efficiency.
However, 65% of surveyed IT decision-makers reveal they have “wasted significant IT spend due to cloud inefficiencies” and only 20% of respondents have a holistic strategy in place when it comes to their transformation. The report identifies the most common causes of unforeseen costs and details how businesses can overcome these hurdles to succeed and drive business growth. The top causes of unforeseen costs include the following:
- Lack of familiarity with the cloud – Limited internal knowledge, expertise and resources are obstacles to managing cloud effectively.
- Runaway cloud costs – When businesses do not configure the cloud to scale up and down effectively, they often consume more resources than predicted.
- The ‘Hotel California of Cloud’ effect – Cloud is temptingly easy to enter, but hard to leave. To avoid egress charges, planning and expertise are crucial to choosing the best cloud infrastructure for workloads.
- Hybrid complexity – Mixing hybrid, multi-cloud and legacy infrastructure platforms has its own additional management costs associated to it.
- Cloud modernization – Organizations are increasingly looking to modernize their cloud applications. However, lack of expertise and legacy systems often add complexity and costs for those looking to do this.
- Wrong consumption model – Companies unfamiliar with cloud may find themselves adopting the wrong consumption model.
“Unforeseen costs associated with the cloud can be a challenge for many businesses that lack a comprehensive cloud strategy. Typically, unanticipated costs come about due to a lack of familiarity with the cloud,” said Marvin Sharp, Vice President of Product & Strategy, Aptum. “Businesses don’t always fully understand how consumption models work and which one is best for their organization. For example, the original migration can often cause a peak in price due to lack of successful refactoring of applications. This price increase can be large, and isn’t always explained to businesses, causing unnecessary concern.”
The full report provides detailed insight into the true cost of cloud, and calls for businesses to optimize their cloud environment and make the most of their cloud budgets.
To see the full findings from part three of Aptum’s Cloud Impact Study 2022, Taking Control of Cloud Costs, download the report here: https://aptum.com/cloud-hub/2022-cis-part-3/.
To see the full findings from part two of Aptum’s Cloud Impact Study 2022, Solving the Security Equation, download the report here: https://aptum.com/cloud-hub/2022-cis-part-2/.
For part one of the report, Hybrid: Why and How– Applying Lessons from Digital Transformation, visit here: https://aptum.com/cloud-hub/2022-cis-part-1/.
The study canvassed the opinions and approaches to cloud technology of 400 senior IT professionals. Respondents were from organizations with 250+ employees in the U.S., Canada and UK. Industries included financial services, technology, telecommunications, manufacturing, retail, public education, and the commercial sector.





